The metallicities of the smallest stars are particularly difficult to determine due to their faint magnitudes and complicated spectra. These cool dwarfs are some of the most common stars in the galaxy, however, so their abundances are particularly useful both for detailed Galactic chemical evolution models and for understanding the exoplanets orbiting small stars.
APOGEE is a component of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey focused on determining stellar parameters as a probe of our Galaxy’s structure and evolution. The APOGEE survey consists mid-resolution infrared spectroscopy fit by a model grid to obtain surface temperatures, gravities, and abundance patterns. APOGEE focuses mostly on giant stars, but has also observed thousands of cool (K and M) dwarfs.
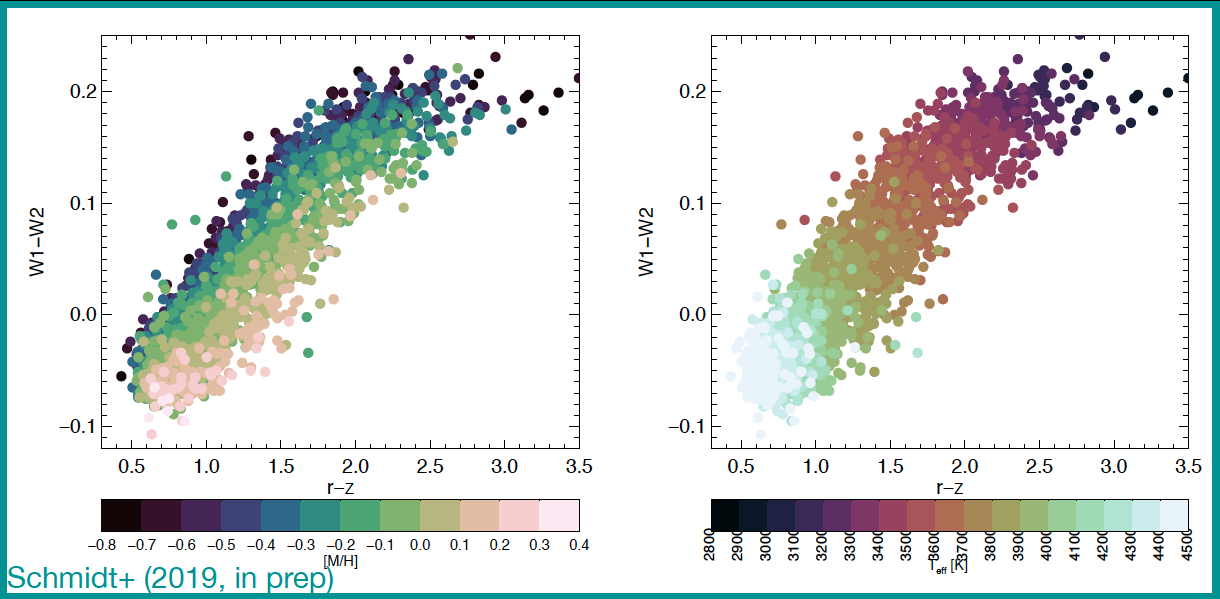
In 2015, I worked with an initial sample of these KM dwarfs to confirm their catalog parameters, compare stellar models, and look for optimal colors for photometric indicators of metallicity and surface temperature. We found that previous stellar models didn’t match the coolest M dwarfs, and we also found strong correlations between SDSS r-z color, WISE W1-W2 color, and these fundamental stellar parameters.
WISE W1-W2 color as a function of SDSS r-z color shown with colors indicating effective temperatures and metallicities from the SDSS APOGEE ASPCAP catalog. This color combination separates metallicity and temperature in different directions, allowing characterization of both properties using photometry alone. From Schmidt et al. 2020.
Since the initial work, the APOGEE data set has doubled and Gaia has released parallaxes for the majority of these nearby stars, and I am working with Jennifer Johnson and Victoria DiTomasso to update and expand the APOGEE KM dwarf project and apply the metallicity indicators to a sample of a million M dwarfs in the Solar neighborhood. Expect new results soon!
-
Examining the relationships between colour, T_eff, and [M/H] for APOGEE K and M dwarfs
Sarah J. Schmidt, Erika L. Wagoner, Jennifer A. Johnson, James R. A. Davenport, Keivan G. Stassun, Diogo Souto, and Jian Ge
MNRAS, Aug 2016
We present the effective temperatures (Teff), metallicities, and colours in Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS), Two Micron All Sky Survey, and Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer filters, of a sample of 3834 late-K and early-M dwarfs selected from the SDSS Apache Point Observatory Galactic Evolution Experiment (APOGEE) spectroscopic survey ASPCAP (APOGEE Stellar Parameters and Chemical Abundances Pipeline) catalogue. We confirm that ASPCAP Teff values between 3550 < Teff < 4200 K are accurate to ̃100 K compared to interferometric Teff values. In that same Teff range, ASPCAP metallicities are accurate to 0.18 dex between -1.0 <[M/H]<0.2. For these cool dwarfs, nearly every colour is sensitive to both Teff and metallicity. Notably, we find that g - r is not a good indicator of metallicity for near-solar metallicity early-M dwarfs. We confirm that J - KS colour is strongly dependent on metallicity, and find that W1 - W2 colour is a promising metallicity indicator. Comparison of the late-K and early-M dwarf colours, metallicities, and Teff to those from three different model grids shows reasonable agreement in r - z and J - KS colours, but poor agreement in u - g, g - r, and W1 - W2. Comparison of the metallicities of the KM dwarf sample to those from previous colour-metallicity relations reveals a lack of consensus in photometric metallicity indicators for late-K and early-M dwarfs. We also present empirical relations for Teff as a function of r - z colour combined with either [M/H] or W1 - W2 colour, and for [M/H] as a function of r - z and W1 - W2 colour. These relations yield Teff to ̃100 K and [M/H] to ̃0.18 dex precision with colours alone, for Teff in the range of 3550-4200 K and [M/H] in the range of -0.5-0.2.